最近はRaspbery PiよりもArduino Unoの方をよく使う。
最初はネットワークがないのがアレだなと思っていたのだが、
実験のようなことをする場合はArduinoの方が何かと便利である。
アナログ入出力がある。
スケッチ例が用意されている。
起動が速い。
shutdownせずに電源を落とせる。
安い。
など。
Arduinoや電子パーツに親しんできて、以前から知ってはいたが手を出さずにいた、
aitendoの「びんぼうでいいの」を買った。
aitendoではキットをいくつか買って作ってみたのだが、びんぼうでいいのを使って
動かす例が紹介されているものが多い。
今まではそれをarduinoで動かしていた。
安いし、2台あってもいいなと思った。
びんぼうでいいのは部品を自分ではんだ付けするものと、実装済みのものがある。
また、実装済みのものにはブートローダ書き込み済みのものと未書き込みのものがある。
私が買ったのは部品実装済みでブートローダ未書き込みのもので、
1120円だった。
http://www.aitendo.com/product/13649
部品実装済みではあるが、ピンソケットとピンヘッダははんだ付けする必要がある。
ピンソケットを付ける穴が2列になっているが、WEBの写真通り外側に付けた。
電源はUSBをつなぐのでDCジャックは付けなかった。
また、マイクロUSBコネクタははんだ付けが不完全なので補強してくださいという注意書きがWEBに記載されている。
aitendoらしい。
でも、こんなことは全然気にならない。喜んで補強した。
そしてそこで気づいたのだが、
USBポートがarduinoはUSB BタイプであるがbinbodeiinoはマイクロUSBである。
ブートローダ書き込みの方法はWEBに記載されている。
少し手間取ったのだが、ちゃんと読むと書いてある通りにすればできる。
binbodeiinoのブートローダ書き込みについて検索するといろいろ情報があり、接続が違う方法などが紹介されていたりする。
いくつかやり方があるのかもしれないしバージョンとか機種とかによるのかもしれないが、とりあえずArduino Unoとびんぼうでいいの(S)ではうまくいった。
接続は
Arduino ---- binbodeiino
13 ---- 13
12 ---- 12
11 ---- 11
10 ---- Reset
5V ---- 5V
GND ---- GND
arduinoのIDEを起動する。
書き込む側のarduinoにスケッチ例の「11. ArduinoISP - ArduinoISP」を書き込む。
IDEの「ツール」ー「ボード」と「ポート」が、書き込む側のarduinoのものになっていることを確認し、「書込装置」に「Arduino as ISP」を選択する。
「ブートローダ書き込み」を実行する。
以下のようなエラーが出たのだが、配線が違っていたり、
書き込み側にArduinoISPのスケッチをアップロードしていなかったりなどが原因で、
WEBで検索すると出てくるような特定のファイルを書き換えるとかいうことは一切必要なかった。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
avrdude: Yikes! Invalid device signature.
Double check connections and try again, or use -F to override
this check.
ブートローダの書き込み中にエラーが発生しました。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
このエラーが出ても、正しい接続と手順で再実行すれば問題なく書き込める。
ブートローダを書き込んだbinbodeiinoをUSBケーブルでPCに接続すると、私のPCでは
デバイスマネージャーで「USB-SERIAL CH340(COM6)」として認識された。
今まであまり意識していなかったが、実装されているマイコンを見てみた。
心臓部といえる部品である。
Arduinoは ATMEGA328P-PU
binbodeiinoは MEGA328P
328Pが同じだし同等品なのだろうが大きさが全然違う。
いくつかサンプルスケッチを動かしてみたが問題なく動いた。
しばらくこれを使ってみる。
このブログを検索
2019/12/31
2019/12/28
トランジスタの動作を実感する
トランジスタの動作を実感する実験。
スイッチを上にすると、330Ωの抵抗とLEDに3.3Vの電圧がかかりLED赤が点灯する。
普通にLEDを点灯する単純な回路。
スイッチを下にすると、トランジスタのベースに電流が流れ、コレクタ・エミッタ間に増幅された電流が流れ、LED青が点灯する。
LEDと10KΩを直列につないで3.3Vの電圧をかけてもLEDは点灯しない。
つまり、LEDを点灯することのできない小さな電流が、LEDを点灯させられるだけの大きな電流に増幅されている。
3.3Vの電圧があってLEDを点灯したいだけならばトランジスタはいらないが、
小さな入力電流があってにそれに応じた大きな出力を作るときに有効である。
2019/12/22
aitendo 基板付きI2CキャラクタLCDモジュール(16x2) [ATD1602CPB]
http://www.aitendo.com/product/17479
組み立て。
部品は少ないが少し迷う。
WEBの写真を見て、バックライトの配線を確認。
バックライトは片面に両面テープがついていたのかもしれない。
そのままつけたのでズレる。
チップコンデンサという小さな部品のはんだ付けをする。
基板の片側に仮はんだ付けをし、そこにチップコンデンサをおいて
片側をはんだ付けした後、反対側をはんだ付けする。
ピンヘッダは付属していないので持っていたものを付ける。
バックライトを使う場合はRLEDをはんだでショットすると書いてあるのでその通りにする
つまり、RLEDと書いてある部分をはんだでつなげる。
配線は書いてある通りに
VDD → 3.3V
SDA → A4
SCL → A5
RST → RESET
VSS → GND
LEDA → 3.3V
「びんぼうでいいの+LCD_ST7032.hライブラリで動作を確認しております。」
と書いてある。
びんぼうでいいの=arduinoに置き換えてよい。
arduinoのIDEを開く。
スケッチ → ライブラリをインクルード → ライブラリを管理...
ライブラリマネージャの検索フィルタに「LCD_ST7032」と入力すると、
LCD_ST7032ライブラリが表示されるので「インストール」をクリック。
ファイル → スケッチ例 の最後の方に「LCD_ST7032」が追加されているので、
その下の「HelloWorld」を選択して実行。
とりあえず動いた。
ときどき文字が左右にあるいは上下に反転する....
どこかはんだ不良があるかな...と半田を直したら、
最初から反転してしまうようになった。
指で触れたりすると正常に戻る。
なんなのこれは。
組み立て。
部品は少ないが少し迷う。
WEBの写真を見て、バックライトの配線を確認。
バックライトは片面に両面テープがついていたのかもしれない。
そのままつけたのでズレる。
チップコンデンサという小さな部品のはんだ付けをする。
基板の片側に仮はんだ付けをし、そこにチップコンデンサをおいて
片側をはんだ付けした後、反対側をはんだ付けする。
ピンヘッダは付属していないので持っていたものを付ける。
バックライトを使う場合はRLEDをはんだでショットすると書いてあるのでその通りにする
つまり、RLEDと書いてある部分をはんだでつなげる。
配線は書いてある通りに
VDD → 3.3V
SDA → A4
SCL → A5
RST → RESET
VSS → GND
LEDA → 3.3V
「びんぼうでいいの+LCD_ST7032.hライブラリで動作を確認しております。」
と書いてある。
びんぼうでいいの=arduinoに置き換えてよい。
arduinoのIDEを開く。
スケッチ → ライブラリをインクルード → ライブラリを管理...
ライブラリマネージャの検索フィルタに「LCD_ST7032」と入力すると、
LCD_ST7032ライブラリが表示されるので「インストール」をクリック。
ファイル → スケッチ例 の最後の方に「LCD_ST7032」が追加されているので、
その下の「HelloWorld」を選択して実行。
とりあえず動いた。
ときどき文字が左右にあるいは上下に反転する....
どこかはんだ不良があるかな...と半田を直したら、
最初から反転してしまうようになった。
指で触れたりすると正常に戻る。
なんなのこれは。
秋月電子 I2C接続キャラクタLCDモジュール 16x2行 白色バックライト付 ACM1602N1-FLW-FBW
参考
http://skomo.o.oo7.jp/f47/hp47_54.htm
ピンヘッダをはんだ付け
各ピンの機能
1(VSS)Ground
2(VDD)3.3V
3(Vo)LCD contrast adjust
4(SCL)SERIAL CLOCK INPUT
5(SDA)SERIAL DATA INPUT
6(BL+)Power supply for BL+
7(BL-)Power supply for BL-
arduino unoとの接続(ブレッドボード)
1 - Ground
2 - 3.3V
3 - 半固定抵抗の真ん中
4 - A4
5 - A5
6 - 3.3V
7 - Ground
半固定抵抗の両端をGround, 3.3Vへ
スケッチ
上記リンクのものをそのまま使って表示できた。
以下に転載
#include <Wire.h>
const char table[]={"From fairest creatures we desire "};
void setup()
{
Wire.begin(); // I2C初期化
LCD_begin();
byte i;
writeCmd(0x80);//ディスプレイON、CURSOR-OFF、blinking-OFF
delay(5);
for(i=0;i<16;i++)
{
writeData(table[i]);
delay();
}
writeCmd(0xC0);//2行目の先頭に移動
delay(5);
for(i=16;i<32;i++)
{
writeData(table[i]);
delay(5);
}
}
void loop() {}
void LCD_begin(void)
{
// LCD初期化
delay(15);
writeCmd(0x01);//クリア ディスプレイ
delay(5);
writeCmd(0x38);//8ビットモード、2ライン、5x8ドット
delay(5);
writeCmd(0x0f);//ディスプレイON、CURSOR-ON、blinking-ON
delay(5);
writeCmd(0x06);//CURSOR移動、スクロールOFF
delay(5);
}
void writeCmd(uint8_t cmd)
{
uint8_t rs_flg;
Wire.beginTransmission(0x50);
rs_flg = 0x00;
Wire.write(rs_flg);
Wire.write(cmd);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void writeData(uint8_t dat)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(0x50);
Wire.write(0x80);
Wire.write(dat);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
http://skomo.o.oo7.jp/f47/hp47_54.htm
ピンヘッダをはんだ付け
各ピンの機能
1(VSS)Ground
2(VDD)3.3V
3(Vo)LCD contrast adjust
4(SCL)SERIAL CLOCK INPUT
5(SDA)SERIAL DATA INPUT
6(BL+)Power supply for BL+
7(BL-)Power supply for BL-
arduino unoとの接続(ブレッドボード)
1 - Ground
2 - 3.3V
3 - 半固定抵抗の真ん中
4 - A4
5 - A5
6 - 3.3V
7 - Ground
半固定抵抗の両端をGround, 3.3Vへ
スケッチ
上記リンクのものをそのまま使って表示できた。
以下に転載
#include <Wire.h>
const char table[]={"From fairest creatures we desire "};
{
Wire.begin(); // I2C初期化
LCD_begin();
byte i;
writeCmd(0x80);//ディスプレイON、CURSOR-OFF、blinking-OFF
delay(5);
for(i=0;i<16;i++)
{
writeData(table[i]);
delay();
}
writeCmd(0xC0);//2行目の先頭に移動
delay(5);
for(i=16;i<32;i++)
{
writeData(table[i]);
delay(5);
}
}
void loop() {}
void LCD_begin(void)
{
// LCD初期化
delay(15);
writeCmd(0x01);//クリア ディスプレイ
delay(5);
writeCmd(0x38);//8ビットモード、2ライン、5x8ドット
delay(5);
writeCmd(0x0f);//ディスプレイON、CURSOR-ON、blinking-ON
delay(5);
writeCmd(0x06);//CURSOR移動、スクロールOFF
delay(5);
}
void writeCmd(uint8_t cmd)
{
uint8_t rs_flg;
Wire.beginTransmission(0x50);
rs_flg = 0x00;
Wire.write(rs_flg);
Wire.write(cmd);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
void writeData(uint8_t dat)
{
Wire.beginTransmission(0x50);
Wire.write(0x80);
Wire.write(dat);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
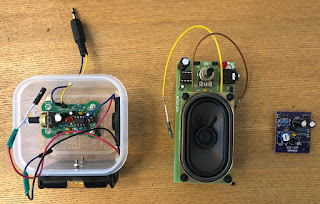
2019/12/21
LM386の発振対策(aitendo スピーカホルダ式アンプキット [K-SPK16X35-386])
LM386の発振について検索してみると、複数の人が「7とGNDの間に10μFのコンデンサを入れる」と書いていたのでやってみたら、「ブー」という雑音はしなくなった。
なぜかはわからないが.......
参考
http://www.tij.co.jp/jp/lit/ds/symlink/lm386.pdf
なぜかはわからないが.......
参考
http://www.tij.co.jp/jp/lit/ds/symlink/lm386.pdf
aitendoのアンプキット
aitendoのアンプキットを3つ作った。
左から
TDA2822アンプキット [K-224B](スピーカー、プラグ、電池ボックスは別売り)
スピーカホルダ式アンプキット [K-SPK16X35-386]
シングルトランジスターアンプ [AKIT-203]
TDA2822はよく鳴る。
Raspberry piのオーディオジャックはそのままだとスピーカーが鳴らないが、
これを通すとよく聞こえた。
AKIT-203はほとんど増幅されない。
何が問題なのだろうか。回路や部品の良しあしはまったくわからない。
そんなに複雑なものでもないので部品のつけ間違い等はないと思う。
AKIT-203はコンデンサが一個足りなくて買ってきた。
入っていたものは 100μF, 25Vだったが、
同じものがなかったので 100μF, 35Vのものを使った。
耐圧が違うと影響あるのだろうか?
可変抵抗がついていて左に回すと音が大きくなるがめいっぱい回しても
大音量で聴いているイヤホンからもれてくるくらいの音しかでない。
可変抵抗は200Kなのだが、大きすぎるのだろうか?
K-SPK16X35-386は音量は十分だがブーというような小さなノイズがずっとある。
音質もあまりよくない。
LM386というICを使っているのだが、発振しやすいことで有名なようだ。
K-224Bを最初に作って、「アンプってこんな簡単な構成で鳴るのか」と感心して
いろいろキットを作ってみているのだが、K-224Bのようにはいかなかった....
2019/12/18
LEDをだんだん明るく・暗くする arduino uno
analogWriteという関数は、pinのON/OFF(HIGH/LOW)という2つの値ではなく、
0から255までの値を設定できる。
それを使ってLEDをだんだん明るくそしてだんだん暗くすることができる。
int a = 0;
void setup()
{
pinMode(9, OUTPUT);
}
void loop()
{
for (a=0; a<255; a++) {
analogWrite(9, a);
delay(10);
}
for (a=255; a>0; a--) {
analogWrite(9, a);
delay(10);
}
}
2019/12/12
2019/12/08
Raspberry Pi 1 Model Bのケースを作った
ベースとなるケースはマルツで数年前に買ったもの。
フタにあいている穴はラジオのケースにしようとして開けたもの。
穴はピンバイスで開けた。
四角い部分は丸い穴をならべて開けてやすりで平らにした。
ピンバイスで穴をたくさんあけるのがキツかったので東急ハンズでドリルを買った。
ついでにM2.6のネジとナットを買って、piにあいている二つの穴を使って固定した。
横に開けた穴は使わないインターフェースだがここを開けないと入らないので開けた。
LANポートがふさがっているがwlanを使っているのでとりあえずいらない。
2019/12/07
Interface 2008年9月号付属の ColdFire基板
先日新宿の紀伊国屋で何を買うでもなくなんかおもしろい本がないかなあと眺めていて、
ラズベリーパイとか電子工作とかその辺の関連の書棚を見ていたら、
「付属ColdFire基板ではじめるEthernet入門」という見出しが表紙に書いてある本があった。中に小さな基板がついていて、そこにRJ-45と電源ジャックをはんだ付けして3.3vのACアダプタを用意すれば使えるとのことであった。
おもしろそうだなと買って帰り、秋葉原に行ったついでに必要な部品等を買ってきた。
RJ-45のジャックは、以下3つの使用を想定しているとのことであった。
Stewart Connector社のSI-600002-F
Pulse社のJ0012D21NL
KINSUN INDUSTRIES社の3070110204
さらっとそれらの型番を検索してみたが見つからない。
秋月にも千石電商にもない。
Pulse社のJ0011D21BNLという型番のものが見つかったので、
想定型番ではないがいけるんじゃないのとはんだ付けしてみたが、
ケーブルをつないでもリンクアップしない。基板も、接続した家のルータのポートもLEDが点灯しない。
ケーブルのせい、ルータのせいを疑っていろいろ試してみたが基板に問題があるとしか思えなかった。
買った本をもう一度よく読んでみる。
Interface(インターフェース) 2008年9月号。
2008年!?
10年以上前だ。
RJ-45のジャックは使えないものがあるので注意みたいなことが書いてある。
J0011D21BNLは、リンクアップや送受信時に点灯するLEDがついている。
これがあるとダメなのか?と思い、秋葉原で買ってきた型番不明のLEDなしのジャックを使ってみようと思い、一度つけたジャックを外そうと思ったのだがハンダ吸いをつかって半田を除去してみたが足が8+2本もあって外れない。
しかたがないので、本をもう一冊買うことにした。
秋葉原の書泉ブックタワーにこの手の本や雑誌があるコーナーがあったなと思い行ってみたが、さすがに2008年のバックナンバーは置いてなかった。
今思うと逆になんで紀伊国屋はこんな古い雑誌を置いていたのだろう....
また紀伊国屋に行ってみるかと思ったがその前にWEBで検索してみると、
Amazonで中古品がたくさん出品されていて価格も安かったので3冊注文した。
そしてノンブランドジャックをはんだ付けしてみたが、やはりダメだ。
2枚の基板をムダにした。あと2枚ある。
やはり指定型番じゃないとダメなのかと、もういちど3つの型番を検索してみると、
Pulse社のJ0012D21NLがmarutsuで買えた。ひとつ1000円くらいだったが3つ買った。
数日後家に届いて、さきほどはんだ付けしたら、ようやくリンクアップした。
192.168.1.0/24 はちょうど家のLANで使っているアドレスで、
基板に設定されている 192.168.1.10 は未使用だったため、
家のルータの空きポートにつなぐと pingが通り、telnetもできた。
Cインタプリタがあったり、いろいろ部品を追加したりできるようなので
これからいじっていきたい。
ラズベリーパイとか電子工作とかその辺の関連の書棚を見ていたら、
「付属ColdFire基板ではじめるEthernet入門」という見出しが表紙に書いてある本があった。中に小さな基板がついていて、そこにRJ-45と電源ジャックをはんだ付けして3.3vのACアダプタを用意すれば使えるとのことであった。
おもしろそうだなと買って帰り、秋葉原に行ったついでに必要な部品等を買ってきた。
RJ-45のジャックは、以下3つの使用を想定しているとのことであった。
Stewart Connector社のSI-600002-F
Pulse社のJ0012D21NL
KINSUN INDUSTRIES社の3070110204
さらっとそれらの型番を検索してみたが見つからない。
秋月にも千石電商にもない。
Pulse社のJ0011D21BNLという型番のものが見つかったので、
想定型番ではないがいけるんじゃないのとはんだ付けしてみたが、
ケーブルをつないでもリンクアップしない。基板も、接続した家のルータのポートもLEDが点灯しない。
ケーブルのせい、ルータのせいを疑っていろいろ試してみたが基板に問題があるとしか思えなかった。
買った本をもう一度よく読んでみる。
Interface(インターフェース) 2008年9月号。
2008年!?
10年以上前だ。
RJ-45のジャックは使えないものがあるので注意みたいなことが書いてある。
J0011D21BNLは、リンクアップや送受信時に点灯するLEDがついている。
これがあるとダメなのか?と思い、秋葉原で買ってきた型番不明のLEDなしのジャックを使ってみようと思い、一度つけたジャックを外そうと思ったのだがハンダ吸いをつかって半田を除去してみたが足が8+2本もあって外れない。
しかたがないので、本をもう一冊買うことにした。
秋葉原の書泉ブックタワーにこの手の本や雑誌があるコーナーがあったなと思い行ってみたが、さすがに2008年のバックナンバーは置いてなかった。
今思うと逆になんで紀伊国屋はこんな古い雑誌を置いていたのだろう....
また紀伊国屋に行ってみるかと思ったがその前にWEBで検索してみると、
Amazonで中古品がたくさん出品されていて価格も安かったので3冊注文した。
そしてノンブランドジャックをはんだ付けしてみたが、やはりダメだ。
2枚の基板をムダにした。あと2枚ある。
やはり指定型番じゃないとダメなのかと、もういちど3つの型番を検索してみると、
Pulse社のJ0012D21NLがmarutsuで買えた。ひとつ1000円くらいだったが3つ買った。
数日後家に届いて、さきほどはんだ付けしたら、ようやくリンクアップした。
192.168.1.0/24 はちょうど家のLANで使っているアドレスで、
基板に設定されている 192.168.1.10 は未使用だったため、
家のルータの空きポートにつなぐと pingが通り、telnetもできた。
Cインタプリタがあったり、いろいろ部品を追加したりできるようなので
これからいじっていきたい。
2019/12/01
raspberry pi 4
またraspberry piを買ってしまった。
4
なんとメモリが4GB
1,2,4から選べるという話だけど、どの店でも4GBしか売ってない。
変わったところは、電源のインタフェースがUSB-Cに
5V 3Aが必要らしい
hdmiがマイクロに
zeroのとき買ったHDMIミニのケーブルを使おうと思っていたが、マイクロだった。
またケーブルを買った。
zeroでさえミニなのに、マイクロにする必要あったのか?
箱を開けて本体を初めて見たとき、「なんか雰囲気が違う!」と感じた。
オーラが違うというか。
普段いれない Raspbian Buster with desktop and recommended software
をSDカードに焼き、
普段やらないがディスプレイ・キーボード・モニタを全部つないで起動
真っ暗な画面が数十秒程度表示されたのち、タイのお寺みたいなきれいなデスクトップが表示された。
おお....
国の選択をして、パスワードを設定して、無線LANのSSIDが自動で検出されるので選んでパスワードを設定する。
ターミナルを起動してraspi-configを起動し、コンソールとsshを有効にする
さらにいつもやらないがvncを有効にする。
RealVNCをWindowsにインストールしてつないでみると
「No matching security types」というエラーでつながらない。
VNCサーバの設定で Option - Security
の Authenticationを 「Unix password」から「VNC password」に変更し、
パスワードを設定したらつながるようになった。
が、今思ったのだが接続するときにアカウントを「pi」にすればつながるんじゃないだろうか?
が、vncで接続アカウントを設定する方法がわからないので
とりあえずこれで行こう。
メモリが4GBにもなって、CPUも新しくなって、漏れ聞こえる情報ではかなりサクサク動き、「パソコンとして使える」ような噂である。
が、そういう使い方はしないだろうな....
4
なんとメモリが4GB
1,2,4から選べるという話だけど、どの店でも4GBしか売ってない。
変わったところは、電源のインタフェースがUSB-Cに
5V 3Aが必要らしい
hdmiがマイクロに
zeroのとき買ったHDMIミニのケーブルを使おうと思っていたが、マイクロだった。
またケーブルを買った。
zeroでさえミニなのに、マイクロにする必要あったのか?
箱を開けて本体を初めて見たとき、「なんか雰囲気が違う!」と感じた。
オーラが違うというか。
普段いれない Raspbian Buster with desktop and recommended software
をSDカードに焼き、
普段やらないがディスプレイ・キーボード・モニタを全部つないで起動
真っ暗な画面が数十秒程度表示されたのち、タイのお寺みたいなきれいなデスクトップが表示された。
おお....
国の選択をして、パスワードを設定して、無線LANのSSIDが自動で検出されるので選んでパスワードを設定する。
ターミナルを起動してraspi-configを起動し、コンソールとsshを有効にする
さらにいつもやらないがvncを有効にする。
RealVNCをWindowsにインストールしてつないでみると
「No matching security types」というエラーでつながらない。
VNCサーバの設定で Option - Security
の Authenticationを 「Unix password」から「VNC password」に変更し、
パスワードを設定したらつながるようになった。
が、今思ったのだが接続するときにアカウントを「pi」にすればつながるんじゃないだろうか?
が、vncで接続アカウントを設定する方法がわからないので
とりあえずこれで行こう。
メモリが4GBにもなって、CPUも新しくなって、漏れ聞こえる情報ではかなりサクサク動き、「パソコンとして使える」ような噂である。
が、そういう使い方はしないだろうな....
2019/11/30
いまどきのraspberry piは /etc/network/interfacesを使わない!!
ちょっとでもハマったら、書く。
私が持っている一番古いラズベリーパイ、B+かな。
今ではそれ対応のケースが売っていない。
SDカードがマイクロじゃない。
wifiがない。
何度か使ったがしばらく使っていなかったのでとりあえずwifiだけつなげとくか、
と触り始めたがつながらない。
まず、いつものようにルータのdhcpアドレス払い出し情報を見るが増えない。
あれー...
無線LANルータを最近変えたのでたぶん設定が古いのだろうとみると、
その通り。
直せばつながる... つながらない........
ifconfigするとwlan0が見えない。
おかしいなあと10分くらいたって、無線LANドングルを挿してないことに気づく。
そうそう、こいつは無線LAN持ってないんだ、えーとこの辺にあったよな....
机の上の箱に入っていたELECOMと書いてあるのを挿す。
lsusbで認識しているのを確認
.....つながらない
ググる。
/etc/network/interfaces に書くんだっけ....
いらなくなったんじゃなかったっけ....
書いてみるがダメ....
wpa_supplicant.conf
dhcpcd.conf
を見直し、普段書かない設定も書いてみる。
ダメ.....
もしかしてこのドングル使えないんじゃ....
違うのを挿す.....「Buffalo」.....
つながった!
ちなみに私はraspberry piは全部家の無線につなぎ固定IPにしている。
結論、/etc/network/interfaces は使わない!
コメントにも dhcpcd.confを使えみたいなことが書いてある!
wifiをつなぐには wpa_supplicant.conf だけ書けばよい!
固定IPにするときは dhcpcd.conf に書く!
dhcpならdhcpと書けばよいと思う!
/etc/network/interfaces は下記のように何も書いてなくてよい!
----------------------
# interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8)
# Please note that this file is written to be used with dhcpcd
# For static IP, consult /etc/dhcpcd.conf and 'man dhcpcd.conf'
# Include files from /etc/network/interfaces.d:
source-directory /etc/network/interfaces.d
----------------------
無線LANドングルは使えるやつを挿せば何もしなくても認識する!
....
調べたら最初に挿したのは WDC-433SU2M2BK
wifiのやつだ。
https://www.elecom.co.jp/products/WDC-433SU2M2BK.html
「5GHz専用」と書いてある。そのせいかな?
使えたのは buffaloの、型番らしきものが見当たらないのだが
たぶん WLI-UC-GNME
https://www.buffalo.jp/product/detail/wli-uc-gnme.html
ついでなのでraspberri pi の型番を確認しておく
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep Revision
https://elinux.org/RPi_HardwareHistory
$ cat /etc/debian_version
10.2
$ cat /etc/issue
Raspbian GNU/Linux 10 \n \l
私が持っている一番古いラズベリーパイ、B+かな。
今ではそれ対応のケースが売っていない。
SDカードがマイクロじゃない。
wifiがない。
何度か使ったがしばらく使っていなかったのでとりあえずwifiだけつなげとくか、
と触り始めたがつながらない。
まず、いつものようにルータのdhcpアドレス払い出し情報を見るが増えない。
あれー...
無線LANルータを最近変えたのでたぶん設定が古いのだろうとみると、
その通り。
直せばつながる... つながらない........
ifconfigするとwlan0が見えない。
おかしいなあと10分くらいたって、無線LANドングルを挿してないことに気づく。
そうそう、こいつは無線LAN持ってないんだ、えーとこの辺にあったよな....
机の上の箱に入っていたELECOMと書いてあるのを挿す。
lsusbで認識しているのを確認
.....つながらない
ググる。
/etc/network/interfaces に書くんだっけ....
いらなくなったんじゃなかったっけ....
書いてみるがダメ....
wpa_supplicant.conf
dhcpcd.conf
を見直し、普段書かない設定も書いてみる。
ダメ.....
もしかしてこのドングル使えないんじゃ....
違うのを挿す.....「Buffalo」.....
つながった!
ちなみに私はraspberry piは全部家の無線につなぎ固定IPにしている。
結論、/etc/network/interfaces は使わない!
コメントにも dhcpcd.confを使えみたいなことが書いてある!
wifiをつなぐには wpa_supplicant.conf だけ書けばよい!
固定IPにするときは dhcpcd.conf に書く!
dhcpならdhcpと書けばよいと思う!
/etc/network/interfaces は下記のように何も書いてなくてよい!
----------------------
# interfaces(5) file used by ifup(8) and ifdown(8)
# Please note that this file is written to be used with dhcpcd
# For static IP, consult /etc/dhcpcd.conf and 'man dhcpcd.conf'
# Include files from /etc/network/interfaces.d:
source-directory /etc/network/interfaces.d
----------------------
無線LANドングルは使えるやつを挿せば何もしなくても認識する!
....
調べたら最初に挿したのは WDC-433SU2M2BK
wifiのやつだ。
https://www.elecom.co.jp/products/WDC-433SU2M2BK.html
「5GHz専用」と書いてある。そのせいかな?
使えたのは buffaloの、型番らしきものが見当たらないのだが
たぶん WLI-UC-GNME
https://www.buffalo.jp/product/detail/wli-uc-gnme.html
ついでなのでraspberri pi の型番を確認しておく
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep Revision
https://elinux.org/RPi_HardwareHistory
を参照
私のは 000e だった。
Raspberry Pi 1 Model B
だ。
の表でもストレージがSDカードになっているから、間違いないだろう。
OSは新しい。最後に入れたのは今年のはず。
$ cat /etc/debian_version
10.2
$ cat /etc/issue
Raspbian GNU/Linux 10 \n \l
2019/11/24
aitendoのLEDランプキット AKIT-0118
aitendoで買ったLEDランプキットを作った。
税別295円。
これくらいならすぐ作れるだろうと思って買ったがずっと放置していたものだ。
部品は、LED8個、マイクロインダクタ1個、定電圧LEDドライバ1個
そして基盤、電源接続用のコード2本
今は「K-8LED004F」という名前になっているようだ。
http://www.aitendo.com/product/6928
基盤に部品をさしてはんだ付けするだけだろ、と思っていたが、
よく見ると基盤の部品間の接続がない。
小さい基盤なので、部品の足を折ってつないだ。
電池ボックスはついていない。
前に買ってあったもの。
単三電池2本で点灯する。
写真だと青っぽいが実際は白だ。
低電圧LEDドライバはトランジスタのような見た目である。
低電圧(3V)でたくさん(8個)のLEDを点灯させることのできる部品だそうだ。
http://www.aitendo.com/product/16776
マイクロインダクタはこの低電圧LEDドライバを使うのに必要である。
インダクタは以前ラジオを作ったときに使ったことがあるが、
見た目は抵抗のようだが実体はコイルである。
電流を蓄える役割があるようなのだが、今回の回路での必要性はよくわからない。
税別295円。
これくらいならすぐ作れるだろうと思って買ったがずっと放置していたものだ。
部品は、LED8個、マイクロインダクタ1個、定電圧LEDドライバ1個
そして基盤、電源接続用のコード2本
今は「K-8LED004F」という名前になっているようだ。
http://www.aitendo.com/product/6928
基盤に部品をさしてはんだ付けするだけだろ、と思っていたが、
よく見ると基盤の部品間の接続がない。
小さい基盤なので、部品の足を折ってつないだ。
電池ボックスはついていない。
前に買ってあったもの。
単三電池2本で点灯する。
写真だと青っぽいが実際は白だ。
低電圧LEDドライバはトランジスタのような見た目である。
低電圧(3V)でたくさん(8個)のLEDを点灯させることのできる部品だそうだ。
http://www.aitendo.com/product/16776
マイクロインダクタはこの低電圧LEDドライバを使うのに必要である。
インダクタは以前ラジオを作ったときに使ったことがあるが、
見た目は抵抗のようだが実体はコイルである。
電流を蓄える役割があるようなのだが、今回の回路での必要性はよくわからない。
2019/11/22
raspberry pi zero wは 2.4GHzにしか対応していない
やっぱラズパイはzeroだよね。
当然w。無線対応。
ネットワークにつながらないpiなんて.....
2個目のpi zero wをセットアップした。
以前etcherではうまくいかなかったのだが、今は問題ない。
imageをSDに書き込むと、windowsで認識されなくなった。
(フォーマットしなさい、となる)
が、SDをいったん「取り外し」て、再度挿すと認識される。
wpa_supplicant.confをwindows上で作ってSDに置く方法をとった。
フレッツのルータでDHCPクライアント情報を見るが増えない。
つながってない...
しかたがないのでキーボードマウスディスプレイをつなぐ。
/etc/network/interfacesとか /etc/dhcpcd.confとかいじってみる。
wpa_supplicant.confに country=JP を入れてみる...
windowsで作った wpa_supplicant.confは行末に ^M がついているので消す...
が、つながらない。
すでにつながっているzero wの設定を見る。
パスワードが平文で書いてある... でも別にそれは関係ないよな...
でもつながっているので設定を同じにしようと見ていたら、
SSIDが 2.4GHzのものになっていた。
そうだ、zero wの無線は2.4GHzにしか対応していなかったのだ!
/etc/network/interfaces とか dhcpcd.confとか country=JPとか関係ない。
wpa_supplicant.confさえちゃんと書けば、zero wの無線はつながる。
当然w。無線対応。
ネットワークにつながらないpiなんて.....
2個目のpi zero wをセットアップした。
以前etcherではうまくいかなかったのだが、今は問題ない。
imageをSDに書き込むと、windowsで認識されなくなった。
(フォーマットしなさい、となる)
が、SDをいったん「取り外し」て、再度挿すと認識される。
wpa_supplicant.confをwindows上で作ってSDに置く方法をとった。
フレッツのルータでDHCPクライアント情報を見るが増えない。
つながってない...
しかたがないのでキーボードマウスディスプレイをつなぐ。
/etc/network/interfacesとか /etc/dhcpcd.confとかいじってみる。
wpa_supplicant.confに country=JP を入れてみる...
windowsで作った wpa_supplicant.confは行末に ^M がついているので消す...
が、つながらない。
すでにつながっているzero wの設定を見る。
パスワードが平文で書いてある... でも別にそれは関係ないよな...
でもつながっているので設定を同じにしようと見ていたら、
SSIDが 2.4GHzのものになっていた。
そうだ、zero wの無線は2.4GHzにしか対応していなかったのだ!
/etc/network/interfaces とか dhcpcd.confとか country=JPとか関係ない。
wpa_supplicant.confさえちゃんと書けば、zero wの無線はつながる。
2019/11/10
LCDのバックライトを点灯する
AQM0802にはバックライトがついている。
値札に記載の商品名にも「バックライト付」と書いてあった。
バックライトのon/offはGPIO4をon/offすればよい。
GPIO4というのはピン番号でいうと3である。
GPIOをon/offするのは以前LEDを点灯させるときにやったので、
その時に作ったスクリプトを元に作った。
---
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import sys
x = int(sys.argv[1])
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(4, GPIO.OUT)
if (x>0):
print('back light on')
GPIO.output(4, True)
else:
print('back light off')
GPIO.output(4, False)
GPIO.cleanup()
---
引数に0を指定するとオフ、1(0より大きい)だとオン
バックライトが光った!
GPIO.cleanupを実行するとバックライトが消えてしまうので、
オンにするときはcleanupしない。
すると、オフにするときに以下のようなwarningが出る。
backlight.py:9: RuntimeWarning: This channel is already in use, continuing anyway. Use GPIO.setwarnings(False) to disable warnings.
warningを消す方法が書いてあるくらいだから、気にしなくていいか。
値札に記載の商品名にも「バックライト付」と書いてあった。
バックライトのon/offはGPIO4をon/offすればよい。
GPIO4というのはピン番号でいうと3である。
GPIOをon/offするのは以前LEDを点灯させるときにやったので、
その時に作ったスクリプトを元に作った。
---
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import sys
x = int(sys.argv[1])
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
GPIO.setup(4, GPIO.OUT)
if (x>0):
print('back light on')
GPIO.output(4, True)
else:
print('back light off')
GPIO.output(4, False)
GPIO.cleanup()
---
引数に0を指定するとオフ、1(0より大きい)だとオン
バックライトが光った!
GPIO.cleanupを実行するとバックライトが消えてしまうので、
オンにするときはcleanupしない。
すると、オフにするときに以下のようなwarningが出る。
backlight.py:9: RuntimeWarning: This channel is already in use, continuing anyway. Use GPIO.setwarnings(False) to disable warnings.
warningを消す方法が書いてあるくらいだから、気にしなくていいか。
2019/11/09
Raspberry Pi zeroでLCDディスプレイに文字を表示する
秋葉原に行って、秋月電子でRaspberry pi用のキャラクタLCDキットを買ってきた。
800何十円だった。
I2C液晶は AQM0802Aというもので8文字 x 2列表示できる。
それをラズパイに接続させるための変換基盤(PCA9515)と、ピンヘッダにさすためのソケットがついていて、液晶とソケットをはんだ付けする。
私ははんだ付けはあまりしないのでヘタクソで不安だったので、
WEBで調べたが簡単なので説明すらされていなかった。
案の定、液晶を基盤に接続するときに隣合ったピンがくっついてしまった。
くっついたところは半田をあたためながら楊枝でなんとか切り離した。
piはzeroを使った。
まず、raspi-configで
5 Interfacing Options
P5 I2C を選んでenableにする。
i2cdetectというコマンドで認識しているか確認するのだが
インストールされていなかったので
sudo apt-get install i2c-tools
はんだ付けしたソケットをpiのGPIOに挿す。
GPIOの1,3,5,7,9,11 を使う。
SDカードがある側を上にして、左の列の上から6本だ。
ちなみに基盤の各ピンに対応する箇所には以下のように書かれている
1: 3V3
3: SDA
5: SCL
7: LED
9: GND
11: RST
sudo i2cdetect -y 1
以下のような内容であれば正常だそうだ。
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3e --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
これで使用できる状態なので早速なにか表示したいが、
WEBを探すとスクリプトが紹介されていたので、
IPアドレスとか任意の文字列を表示させてみた。
スクリプトではコマンド実行結果を加工したり任意の文字列をコマンドにわたせる型に変換したりしているのだが、
コマンドそのものの使い方を調べてみた。
Usage: i2cset [-f] [-y] [-m MASK] [-r] I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS [VALUE] ... [MODE]
I2CBUS is an integer or an I2C bus name
ADDRESS is an integer (0x03 - 0x77)
MODE is one of:
c (byte, no value)
b (byte data, default)
w (word data)
i (I2C block data)
s (SMBus block data)
Append p for SMBus PEC
まず初期化する。
以下2行がお決まりの初期化コマンドのようだ。
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0 0x38 0x39 0x14 0x70 0x56 0x6c i
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0 0x38 0x0d 0x01 i
0x3e というのが書き込み対象(I2CBUS)、i2cdetectで表示されていた値だ。
i は「block data」、連続してデータを書き込む指定である。
文字コードは下記に記載がある。
http://akizukidenshi.com/download/ds/xiamen/AQM0802.pdf
#全部消して1行目の最初にカーソル移動
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0 0x38 0x0d 0x01 i
#指定したデータを連続して表示
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0x40 [data1] [data2] [data3] i
#改行してカーソルを先頭に移動
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0x00 0xc0 i
8文字入力したらコマンドで改行しないと折り返さない。
#「Hello」と表示
800何十円だった。
I2C液晶は AQM0802Aというもので8文字 x 2列表示できる。
それをラズパイに接続させるための変換基盤(PCA9515)と、ピンヘッダにさすためのソケットがついていて、液晶とソケットをはんだ付けする。
私ははんだ付けはあまりしないのでヘタクソで不安だったので、
WEBで調べたが簡単なので説明すらされていなかった。
案の定、液晶を基盤に接続するときに隣合ったピンがくっついてしまった。
くっついたところは半田をあたためながら楊枝でなんとか切り離した。
piはzeroを使った。
まず、raspi-configで
5 Interfacing Options
P5 I2C を選んでenableにする。
i2cdetectというコマンドで認識しているか確認するのだが
インストールされていなかったので
sudo apt-get install i2c-tools
はんだ付けしたソケットをpiのGPIOに挿す。
GPIOの1,3,5,7,9,11 を使う。
SDカードがある側を上にして、左の列の上から6本だ。
ちなみに基盤の各ピンに対応する箇所には以下のように書かれている
1: 3V3
3: SDA
5: SCL
7: LED
9: GND
11: RST
sudo i2cdetect -y 1
以下のような内容であれば正常だそうだ。
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- 3e --
40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
これで使用できる状態なので早速なにか表示したいが、
WEBを探すとスクリプトが紹介されていたので、
IPアドレスとか任意の文字列を表示させてみた。
スクリプトではコマンド実行結果を加工したり任意の文字列をコマンドにわたせる型に変換したりしているのだが、
コマンドそのものの使い方を調べてみた。
Usage: i2cset [-f] [-y] [-m MASK] [-r] I2CBUS CHIP-ADDRESS DATA-ADDRESS [VALUE] ... [MODE]
I2CBUS is an integer or an I2C bus name
ADDRESS is an integer (0x03 - 0x77)
MODE is one of:
c (byte, no value)
b (byte data, default)
w (word data)
i (I2C block data)
s (SMBus block data)
Append p for SMBus PEC
まず初期化する。
以下2行がお決まりの初期化コマンドのようだ。
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0 0x38 0x39 0x14 0x70 0x56 0x6c i
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0 0x38 0x0d 0x01 i
0x3e というのが書き込み対象(I2CBUS)、i2cdetectで表示されていた値だ。
i は「block data」、連続してデータを書き込む指定である。
文字コードは下記に記載がある。
http://akizukidenshi.com/download/ds/xiamen/AQM0802.pdf
#全部消して1行目の最初にカーソル移動
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0 0x38 0x0d 0x01 i
#指定したデータを連続して表示
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0x40 [data1] [data2] [data3] i
#改行してカーソルを先頭に移動
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0x00 0xc0 i
8文字入力したらコマンドで改行しないと折り返さない。
#「Hello」と表示
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0x40 0x48 0x65 0x6c 0x6c 0x6f i
#「トウキョウ」と表示
sudo i2cset -y 1 0x3e 0x40 0xc4 0xb3 0xb7 0xae 0xb3 i
2019/10/18
パソコンが不定期にビープを鳴らす
PCパーツを一新したら、時々、数時間に一回くらい、ピッ、ピッ、ピッ、ピッというビープ音がなるようになった。
短いビープがだいたい4回、1秒間隔くらいで鳴る。
PCは常に電源をいれたままにしているが、鳴るのはだいたい寝る前、PCを使っておらず隣の部屋にいるときだ。
しかるべきワードで検索するとまず出てくるのは起動時にビープがなって起動しない、という情報だが、私の場合はすでに起動しているときで、ビープがなるだけで普通に使えている。
また、システムに負担がかかっているとかではなく、むしろ何もしていないときに鳴る。
まず思い当たるのは電源容量不足だ。
電源ユニットは1年前に買ったばかりで結構よいものを買ってあったので、よく調べずに大丈夫だろうと流用したが、必要な容量の2倍くらいがよい、などの情報もあって少し不安だった。
動作自体は特に問題ない。
6万円くらいかけて一新したほどの違いもないのだが。
だんだん鳴る頻度が高くなってきたように感じる。
夕べは夜中に鳴って、ずっと鳴りやまず起きてしまった。
ハードディスクの電源を一つ抜いた。
ASRockのユーティリティをダウンロードし、マザーボードのBIOS以外の新しいソフトウェアをすべてインストールした。
BIOSは現状に問題がなければインストールしないほうがよい、との注意書きがあったので。
それから、調べたらメモリの問題も疑われたので、いったん外して付け直した。
短いビープがだいたい4回、1秒間隔くらいで鳴る。
PCは常に電源をいれたままにしているが、鳴るのはだいたい寝る前、PCを使っておらず隣の部屋にいるときだ。
しかるべきワードで検索するとまず出てくるのは起動時にビープがなって起動しない、という情報だが、私の場合はすでに起動しているときで、ビープがなるだけで普通に使えている。
また、システムに負担がかかっているとかではなく、むしろ何もしていないときに鳴る。
まず思い当たるのは電源容量不足だ。
電源ユニットは1年前に買ったばかりで結構よいものを買ってあったので、よく調べずに大丈夫だろうと流用したが、必要な容量の2倍くらいがよい、などの情報もあって少し不安だった。
動作自体は特に問題ない。
6万円くらいかけて一新したほどの違いもないのだが。
だんだん鳴る頻度が高くなってきたように感じる。
夕べは夜中に鳴って、ずっと鳴りやまず起きてしまった。
ハードディスクの電源を一つ抜いた。
ASRockのユーティリティをダウンロードし、マザーボードのBIOS以外の新しいソフトウェアをすべてインストールした。
BIOSは現状に問題がなければインストールしないほうがよい、との注意書きがあったので。
それから、調べたらメモリの問題も疑われたので、いったん外して付け直した。
2019/10/15
raspivid と ffmpegでyoutubeにリアルタイムライブ配信
簡単にできた。
raspivid -o - -t 0 -vf -hf -fps 30 -b 6000000 | ffmpeg -re -ar 44100 -ac 2 -acodec pcm_s16le -f s16le -ac 2 -i /dev/zero -f h264 -i - -vcodec copy -acodec aac -ab 128k -g 50 -strict experimental -f flv [ストリームURL]/[ストリームキー]
raspivid -o - -t 0 -vf -hf -fps 30 -b 6000000 | ffmpeg -re -ar 44100 -ac 2 -acodec pcm_s16le -f s16le -ac 2 -i /dev/zero -f h264 -i - -vcodec copy -acodec aac -ab 128k -g 50 -strict experimental -f flv [ストリームURL]/[ストリームキー]
2019/10/14
vlcでストリーミングはLANのみうまくいくがインターネット越しではダメ
ffmpeg のストリーミングはうまくいかない。
ほかの方法を試す。
vlcをpiにインストール
sudo apt install vlc
raspivid -w 640 -h 480 \
-o - -t 0 -n \
| cvlc -vvv stream:///dev/stdin \
--sout '#rtp{sdp=rtsp://:5963/}' :demux=h264
クライアントでvlcを起動し、
ほかの方法を試す。
vlcをpiにインストール
sudo apt install vlc
インストールできたら下記を実行
-o - -t 0 -n \
| cvlc -vvv stream:///dev/stdin \
--sout '#rtp{sdp=rtsp://:5963/}' :demux=h264
クライアントでvlcを起動し、
[メディア]-[ネットワークストリームを開く]
URLに 以下を入力して[再生]
rtsp://192.168.xx.xx:5963/
192.168.xx.xxはpiのipアドレス、最後のスラッシュがないとダメ
見えた!
それではmotionの時と同様にインターネット経由で外部から観ることができるようにしよう.....
フレッツルータで静的IPマスカレードを設定する。
tcp:5963を開ける。
ダメ。
UDPも開ける。
ダメ。
IPが変わっていた...直す。ダメ。
フレッツルータで全プロトコルを転送する設定にするがそれでもダメ。
真っ暗な画面だけが表示される。
pi側にインターネット越しに接続しているログは出るが....
-w/-hや-fpsをいろいろ変えてもダメ.....
rtspで配信してvlcで観る、というのをやっている人はいても、
インターネットから観ている人がいない.....
それではmotionの時と同様にインターネット経由で外部から観ることができるようにしよう.....
フレッツルータで静的IPマスカレードを設定する。
tcp:5963を開ける。
ダメ。
UDPも開ける。
ダメ。
IPが変わっていた...直す。ダメ。
フレッツルータで全プロトコルを転送する設定にするがそれでもダメ。
真っ暗な画面だけが表示される。
pi側にインターネット越しに接続しているログは出るが....
-w/-hや-fpsをいろいろ変えてもダメ.....
rtspで配信してvlcで観る、というのをやっている人はいても、
インターネットから観ている人がいない.....
ffmpeg
raspberry piにカメラをつけて、motionをインストールして
WindowsやiPhoneのブラウザで見ている。
motionの場合は、クライアントからraspberry piへアクセスする必要がある。
raspberry piは家にある。家はフレッツ回線でインターネット接続している。
フレッツのルータのポートフォワーディング(「静的IPマスカレード」)設定により、フレッツで割り当てられているグローバルIPアドレス宛にアクセスして、ルータによりLAN内のraspberry piに転送されている。
グローバルIPアドレスは変更されることもあるし、そもそも外部から自宅のネットワーク内にアクセスさせていることはあまりよくない。
台風が来た時にyoutubeにライブ映像がたくさんあるのを見て、
きっと簡単にできるに違いないと思いしらべてみると、
ffmpegを使うという情報がたくさん出てきた。
ところが、公開されている情報のとおりにやってみようとしてもなかなかうまくいかない。
ffmpegの基本的な動作から確認していこうと思う。
ffmpeg -f v4l2 -i /dev/video0 -c:v h264_omx -c:a aac -f matroska out.mkv
これはできた。
カメラの画像を.mkv形式の動画ファイルとして出力するものだ。
-i /dev/video0 は動画の入力デバイス。
out.mkv は出力ファイル名。
-c:v はビデオコーデック、 -c:a はオーディオコーデックか。
最初の -f v4l2 は、入力フォーマット、v4l2は Video for Linux version2
後ろの -f matroska は出力フォーマット
コマンドを実行すると、以下のように表示される。
(色や太字などはわかりやすいように変えた)
pi:~ $ ffmpeg -f v4l2 -i /dev/video0 -c:v h264_omx -c:a aac -f matroska out.mkv
ffmpeg version 3.2.14-1~deb9u1+rpt1 Copyright (c) 2000-2019 the FFmpeg developers
built with gcc 6.3.0 (Raspbian 6.3.0-18+rpi1+deb9u1) 20170516
configuration: --prefix=/usr --extra-version='1~deb9u1+rpt1' --toolchain=hardened --libdir=/usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf --incdir=/usr/include/arm-linux-gnueabihf --enable-gpl --disable-stripping --enable-avresample --enable-avisynth --enable-gnutls --enable-ladspa --enable-libass --enable-libbluray --enable-libbs2b --enable-libcaca --enable-libcdio --enable-libebur128 --enable-libflite --enable-libfontconfig --enable-libfreetype --enable-libfribidi --enable-libgme --enable-libgsm --enable-libmp3lame --enable-libopenjpeg --enable-libopenmpt --enable-libopus --enable-libpulse --enable-librubberband --enable-libshine --enable-libsnappy --enable-libsoxr --enable-libspeex --enable-libssh --enable-libtheora --enable-libtwolame --enable-libvorbis --enable-libvpx --enable-libwavpack --enable-libwebp --enable-libx265 --enable-libxvid --enable-libzmq --enable-libzvbi --enable-omx --enable-omx-rpi --enable-mmal --enable-openal --enable-opengl --enable-sdl2 --enable-libdc1394 --enable-libiec61883 --arch=armhf --enable-chromaprint --enable-frei0r --enable-libopencv --enable-libx264 --enable-shared
libavutil 55. 34.101 / 55. 34.101
libavcodec 57. 64.101 / 57. 64.101
libavformat 57. 56.101 / 57. 56.101
libavdevice 57. 1.100 / 57. 1.100
libavfilter 6. 65.100 / 6. 65.100
libavresample 3. 1. 0 / 3. 1. 0
libswscale 4. 2.100 / 4. 2.100
libswresample 2. 3.100 / 2. 3.100
libpostproc 54. 1.100 / 54. 1.100
Input #0, video4linux2,v4l2, from '/dev/video0':
Duration: N/A, start: 1487.474279, bitrate: 283115 kb/s
Stream #0:0: Video: rawvideo (I420 / 0x30323449), yuv420p, 1024x768, 283115 kb/s, 30 fps, 30 tbr, 1000k tbn, 1000k tbc
[h264_omx @ 0x1215bb0] Using OMX.broadcom.video_encode
Output #0, matroska, to 'out2.mkv':
Metadata:
encoder : Lavf57.56.101
Stream #0:0: Video: h264 (h264_omx) (H264 / 0x34363248), yuv420p, 1024x768, q=2-31, 200 kb/s, 30 fps, 1k tbn, 30 tbc
Metadata:
encoder : Lavc57.64.101 h264_omx
Stream mapping:
Stream #0:0 -> #0:0 (rawvideo (native) -> h264 (h264_omx))
Press [q] to stop, [?] for help
frame= 16 fps=2.6 q=-0.0 Lsize= 13kB time=00:00:06.16 bitrate= 17.9kbits/s speed=0.989x
最後の行(緑色)は時間の経過とともに更新されて、q を押すと停止する。
video:13kB audio:0kB subtitle:0kB other streams:0kB global headers:0kB muxing overhead: 7.172307%
このpiにはマイクがないので、オーディオは録音されない。
出力された out.mkvをマウントしているWindowsの共有フォルダにコピーし、
vlcメディアプレイヤーで動画が再生できた。
ffmpegにはたくさんのパラメータがあって、出力をファイルではなくストリーミングにすることができるのである。
そんなに難しいことはないはず......
WindowsやiPhoneのブラウザで見ている。
motionの場合は、クライアントからraspberry piへアクセスする必要がある。
raspberry piは家にある。家はフレッツ回線でインターネット接続している。
フレッツのルータのポートフォワーディング(「静的IPマスカレード」)設定により、フレッツで割り当てられているグローバルIPアドレス宛にアクセスして、ルータによりLAN内のraspberry piに転送されている。
グローバルIPアドレスは変更されることもあるし、そもそも外部から自宅のネットワーク内にアクセスさせていることはあまりよくない。
台風が来た時にyoutubeにライブ映像がたくさんあるのを見て、
きっと簡単にできるに違いないと思いしらべてみると、
ffmpegを使うという情報がたくさん出てきた。
ところが、公開されている情報のとおりにやってみようとしてもなかなかうまくいかない。
ffmpegの基本的な動作から確認していこうと思う。
ffmpeg -f v4l2 -i /dev/video0 -c:v h264_omx -c:a aac -f matroska out.mkv
これはできた。
カメラの画像を.mkv形式の動画ファイルとして出力するものだ。
-i /dev/video0 は動画の入力デバイス。
out.mkv は出力ファイル名。
-c:v はビデオコーデック、 -c:a はオーディオコーデックか。
最初の -f v4l2 は、入力フォーマット、v4l2は Video for Linux version2
後ろの -f matroska は出力フォーマット
コマンドを実行すると、以下のように表示される。
(色や太字などはわかりやすいように変えた)
pi:~ $ ffmpeg -f v4l2 -i /dev/video0 -c:v h264_omx -c:a aac -f matroska out.mkv
ffmpeg version 3.2.14-1~deb9u1+rpt1 Copyright (c) 2000-2019 the FFmpeg developers
built with gcc 6.3.0 (Raspbian 6.3.0-18+rpi1+deb9u1) 20170516
configuration: --prefix=/usr --extra-version='1~deb9u1+rpt1' --toolchain=hardened --libdir=/usr/lib/arm-linux-gnueabihf --incdir=/usr/include/arm-linux-gnueabihf --enable-gpl --disable-stripping --enable-avresample --enable-avisynth --enable-gnutls --enable-ladspa --enable-libass --enable-libbluray --enable-libbs2b --enable-libcaca --enable-libcdio --enable-libebur128 --enable-libflite --enable-libfontconfig --enable-libfreetype --enable-libfribidi --enable-libgme --enable-libgsm --enable-libmp3lame --enable-libopenjpeg --enable-libopenmpt --enable-libopus --enable-libpulse --enable-librubberband --enable-libshine --enable-libsnappy --enable-libsoxr --enable-libspeex --enable-libssh --enable-libtheora --enable-libtwolame --enable-libvorbis --enable-libvpx --enable-libwavpack --enable-libwebp --enable-libx265 --enable-libxvid --enable-libzmq --enable-libzvbi --enable-omx --enable-omx-rpi --enable-mmal --enable-openal --enable-opengl --enable-sdl2 --enable-libdc1394 --enable-libiec61883 --arch=armhf --enable-chromaprint --enable-frei0r --enable-libopencv --enable-libx264 --enable-shared
libavutil 55. 34.101 / 55. 34.101
libavcodec 57. 64.101 / 57. 64.101
libavformat 57. 56.101 / 57. 56.101
libavdevice 57. 1.100 / 57. 1.100
libavfilter 6. 65.100 / 6. 65.100
libavresample 3. 1. 0 / 3. 1. 0
libswscale 4. 2.100 / 4. 2.100
libswresample 2. 3.100 / 2. 3.100
libpostproc 54. 1.100 / 54. 1.100
Input #0, video4linux2,v4l2, from '/dev/video0':
Duration: N/A, start: 1487.474279, bitrate: 283115 kb/s
Stream #0:0: Video: rawvideo (I420 / 0x30323449), yuv420p, 1024x768, 283115 kb/s, 30 fps, 30 tbr, 1000k tbn, 1000k tbc
[h264_omx @ 0x1215bb0] Using OMX.broadcom.video_encode
Output #0, matroska, to 'out2.mkv':
Metadata:
encoder : Lavf57.56.101
Stream #0:0: Video: h264 (h264_omx) (H264 / 0x34363248), yuv420p, 1024x768, q=2-31, 200 kb/s, 30 fps, 1k tbn, 30 tbc
Metadata:
encoder : Lavc57.64.101 h264_omx
Stream mapping:
Stream #0:0 -> #0:0 (rawvideo (native) -> h264 (h264_omx))
Press [q] to stop, [?] for help
frame= 16 fps=2.6 q=-0.0 Lsize= 13kB time=00:00:06.16 bitrate= 17.9kbits/s speed=0.989x
最後の行(緑色)は時間の経過とともに更新されて、q を押すと停止する。
video:13kB audio:0kB subtitle:0kB other streams:0kB global headers:0kB muxing overhead: 7.172307%
このpiにはマイクがないので、オーディオは録音されない。
出力された out.mkvをマウントしているWindowsの共有フォルダにコピーし、
vlcメディアプレイヤーで動画が再生できた。
ffmpegにはたくさんのパラメータがあって、出力をファイルではなくストリーミングにすることができるのである。
そんなに難しいことはないはず......
2019/10/12
iphoneのメール設定
いつも忘れるので。
名前: john、ドメイン名: example.com の場合
まず、サーバに john というユーザがあること。
/home/john というフォルダがあること。
メールアドレス john@example.com
メールサーバホスト名(incoming, outgoingともに): mail.example.com
advanced で
INCOMING SETTINGS
Use SSL: on
Authentication: password
server port: 993
OUTGOING MAIL SERVER
Use SSL: on
Authentication: password
Server Port: 587
名前: john、ドメイン名: example.com の場合
まず、サーバに john というユーザがあること。
/home/john というフォルダがあること。
メールアドレス john@example.com
メールサーバホスト名(incoming, outgoingともに): mail.example.com
advanced で
INCOMING SETTINGS
Use SSL: on
Authentication: password
server port: 993
OUTGOING MAIL SERVER
Use SSL: on
Authentication: password
Server Port: 587
2019/10/06
PCを新調
(参考)
マザーボード
ASRock Z390M Pro4
CPU Intel CORE i5-9400F
メモリ 8GBx2
GeIL GSB416GB2666C16ADC
(DDR4 PC4-21330)
SSD(M.2) SSDPEKNW010T8X1 1024GB intel
グラフィックカード 玄人志向 RD-RX560-E2GB/OC REV2.0
以下は流用
電源 1年ほど前に買った antec NeoECO Gold NE550G
TVチューナーボード Xit Board (XIT-BRD100W)
TVチューナーボード Xit Board (XIT-BRD100W)
組み立て・インストールで特にトラブることはなし。
CPUグリスはリテールファンに塗布ずみ。
マザーボードはASRockを使っていたので配置に戸惑うこともなし。
ASRockは3枚目かな。
特に何がいいということはないが、BIOS画面のロゴがシンプルでよい、
ASRockにしてからトラブルがほとんどない、などの理由。
CPUを i5-9400Fにしようと決めて、あとはそれが動くものを集めた。
メモリは8GBx2の組み合わせでドスパラで一番安いやつ
SSDもM.2の1TBで一番安いやつ
グラフィックボードは流用でいいかなと思ったが、
もう5年くらいたっているので新調した。
5000円くらいのものでいいかなと思っていたが逆にそんなものはあまり売ってないので
約1万円のものをツクモで買う。
Windows10のインストールが速攻で終わるが、
アップデートが大量にあるので「最新です」になるまで2時間くらいかかったかな。
アップデート中はPCを使えるようにはなっていたが。
速くはなったが、劇的に速い!と驚くほどでもなし。
やってることがたいしたことではないけど。
やってることがたいしたことではないけど。
画像ファイルをダブルクリックするとWindowsの「フォト」というアプリでプレビュー表示になるのが一瞬で表示されるようになった。
今までは5秒かそれ以上かかっていた。
パーツをどれにしようか選んでいる最中にM.2 SATAなるものがあるのを知った。
これは脅威。まもなく3.5/2.5インチディスクドライブは過去の遺物となるだろう。
今はまだ使っているが。
2019/08/06
WEBカメラの比較
所持しているWEBカメラの比較
ラズベリーパイカメラモジュールv2
800万画素(!)
4680円(スイッチサイエンス)
https://www.switch-science.com/catalog/2713/
(所持していないが参考までに)
ラズベリーパイカメラモジュールv1
500万画素(!)
https://www.switch-science.com/catalog/1432/
ELECOM UCAM-C0220FBBK
200万画素 1600x1200 pixel 固定フォーカス
2700円
https://www2.elecom.co.jp/multimedia/pc-camera/ucam-c0220fb/
BUFFALO BSWHD06M
120万画素 1280x960 pixel マニュアルフォーカス
2660円(1400円で買った)
https://www.buffalo.jp/product/detail/bswhd06mbk.html
Logicool C270 120万画素
2300円くらい
https://kakaku.com/item/K0000138158/
ELECOM UCAM-C310FBBK
100万画素 1280x720 pixel 固定フォーカス
https://www.elecom.co.jp/products/UCAM-C310FBBK.html
logicoolのC270は仕様上の画素数が低いが画質はよい印象がある。
が、個体の不良なのかわからないが頻繁に認識されなくなる。
UCAM-C310FBBKは画質が低すぎる。
とりあえず映る、程度。
ラズパイのカメラモジュールは画質よすぎじゃないのか。
もっと低画質でいいから2000円くらいのを出してほしい。
ちなみにスペック等不明だが、piカメラのコピーモデルのようなものを持っている。
たしか価格は2000円くらい。ボードにRaspberry piとか書いてあるのだが、
どうやらニセモノのようだ。
穴の位置が本物と違うため、カメラ対応ケースにはまらない。
ラズベリーパイカメラモジュールv2
800万画素(!)
4680円(スイッチサイエンス)
https://www.switch-science.com/catalog/2713/
(所持していないが参考までに)
ラズベリーパイカメラモジュールv1
500万画素(!)
https://www.switch-science.com/catalog/1432/
ELECOM UCAM-C0220FBBK
200万画素 1600x1200 pixel 固定フォーカス
2700円
https://www2.elecom.co.jp/multimedia/pc-camera/ucam-c0220fb/
BUFFALO BSWHD06M
120万画素 1280x960 pixel マニュアルフォーカス
2660円(1400円で買った)
https://www.buffalo.jp/product/detail/bswhd06mbk.html
Logicool C270 120万画素
2300円くらい
https://kakaku.com/item/K0000138158/
ELECOM UCAM-C310FBBK
100万画素 1280x720 pixel 固定フォーカス
https://www.elecom.co.jp/products/UCAM-C310FBBK.html
logicoolのC270は仕様上の画素数が低いが画質はよい印象がある。
が、個体の不良なのかわからないが頻繁に認識されなくなる。
UCAM-C310FBBKは画質が低すぎる。
とりあえず映る、程度。
ラズパイのカメラモジュールは画質よすぎじゃないのか。
もっと低画質でいいから2000円くらいのを出してほしい。
ちなみにスペック等不明だが、piカメラのコピーモデルのようなものを持っている。
たしか価格は2000円くらい。ボードにRaspberry piとか書いてあるのだが、
どうやらニセモノのようだ。
穴の位置が本物と違うため、カメラ対応ケースにはまらない。
motion 4.1.1 デフォルトコンフィグ
pi@raspberrypi:~ $ sudo cat /etec/motion/motion.conf
# Rename this distribution example file to motion.conf
#
# This config file was generated by motion 4.1.1
# Documentation: /usr/share/doc/motion/motion_guide.html
############################################################
# Daemon
############################################################
# Start in daemon (background) mode and release terminal (default: off)
daemon off
# File to store the process ID, also called pid file. (default: not defined)
process_id_file /var/run/motion/motion.pid
############################################################
# Basic Setup Mode
############################################################
# Start in Setup-Mode, daemon disabled. (default: off)
setup_mode off
# Use a file to save logs messages, if not defined stderr and syslog is used. (default: not defined)
logfile /var/log/motion/motion.log
# Level of log messages [1..9] (EMG, ALR, CRT, ERR, WRN, NTC, INF, DBG, ALL). (default: 6 / NTC)
log_level 6
# Filter to log messages by type (COR, STR, ENC, NET, DBL, EVT, TRK, VID, ALL). (default: ALL)
log_type all
###########################################################
# Capture device options
############################################################
# Videodevice to be used for capturing (default /dev/video0)
# for FreeBSD default is /dev/bktr0
videodevice /dev/video0
# v4l2_palette allows one to choose preferable palette to be use by motion
# See motion_guide.html for the valid options and values. (default: 17)
v4l2_palette 17
# Tuner device to be used for capturing using tuner as source (default /dev/tuner0)
# This is ONLY used for FreeBSD. Leave it commented out for Linux
; tunerdevice /dev/tuner0
# The video input to be used (default: -1)
# Should normally be set to 0 or 1 for video/TV cards, and -1 for USB cameras
# Set to 0 for uvideo(4) on OpenBSD
input -1
# The video norm to use (only for video capture and TV tuner cards)
# Values: 0 (PAL), 1 (NTSC), 2 (SECAM), 3 (PAL NC no colour). Default: 0 (PAL)
norm 0
# The frequency to set the tuner to (kHz) (only for TV tuner cards) (default: 0)
frequency 0
# Override the power line frequency for the webcam. (normally not necessary)
# Values:
# -1 : Do not modify device setting
# 0 : Power line frequency Disabled
# 1 : 50hz
# 2 : 60hz
# 3 : Auto
power_line_frequency -1
# Rotate image this number of degrees. The rotation affects all saved images as
# well as movies. Valid values: 0 (default = no rotation), 90, 180 and 270.
rotate 0
# Flip image over a given axis (vertical or horizontal), vertical means from left to right
# horizontal means top to bottom. Valid values: none, v and h.
flip_axis none
# Image width (pixels). Valid range: Camera dependent, default: 320
width 320
# Image height (pixels). Valid range: Camera dependent, default: 240
height 240
# Maximum number of frames to be captured per second.
# Valid range: 2-100. Default: 100 (almost no limit).
framerate 2
# Minimum time in seconds between capturing picture frames from the camera.
# Default: 0 = disabled - the capture rate is given by the camera framerate.
# This option is used when you want to capture images at a rate lower than 2 per second.
minimum_frame_time 0
# Full Network Camera URL. Valid Services: http:// ftp:// mjpg:// rtsp:// mjpeg:// file:// rtmp://
; netcam_url value
# Username and password for network camera if required. Syntax is user:password
; netcam_userpass value
# The setting for keep-alive of network socket, should improve performance on compatible net cameras.
# off: The historical implementation using HTTP/1.0, closing the socket after each http request.
# force: Use HTTP/1.0 requests with keep alive header to reuse the same connection.
# on: Use HTTP/1.1 requests that support keep alive as default.
# Default: off
netcam_keepalive off
# URL to use for a netcam proxy server, if required, e.g. "http://myproxy".
# If a port number other than 80 is needed, use "http://myproxy:1234".
# Default: not defined
; netcam_proxy value
# Set less strict jpeg checks for network cameras with a poor/buggy firmware.
# Default: off
netcam_tolerant_check off
# RTSP connection uses TCP to communicate to the camera. Can prevent image corruption.
# Default: on
rtsp_uses_tcp on
# Name of camera to use if you are using a camera accessed through OpenMax/MMAL
# Default: Not defined
; mmalcam_name vc.ril.camera
# Camera control parameters (see raspivid/raspistill tool documentation)
# Default: Not defined
; mmalcam_control_params -hf
# Let motion regulate the brightness of a video device (default: off).
# The auto_brightness feature uses the brightness option as its target value.
# If brightness is zero auto_brightness will adjust to average brightness value 128.
# Only recommended for cameras without auto brightness
auto_brightness off
# Set the initial brightness of a video device.
# If auto_brightness is enabled, this value defines the average brightness level
# which Motion will try and adjust to.
# Valid range 0-255, default 0 = disabled
brightness 0
# Set the contrast of a video device.
# Valid range 0-255, default 0 = disabled
contrast 0
# Set the saturation of a video device.
# Valid range 0-255, default 0 = disabled
saturation 0
# Set the hue of a video device (NTSC feature).
# Valid range 0-255, default 0 = disabled
hue 0
############################################################
# Round Robin (multiple inputs on same video device name)
############################################################
# Number of frames to capture in each roundrobin step (default: 1)
roundrobin_frames 1
# Number of frames to skip before each roundrobin step (default: 1)
roundrobin_skip 1
# Try to filter out noise generated by roundrobin (default: off)
switchfilter off
############################################################
# Motion Detection Settings:
############################################################
# Threshold for number of changed pixels in an image that
# triggers motion detection (default: 1500)
threshold 1500
# Automatically tune the threshold down if possible (default: off)
threshold_tune off
# Noise threshold for the motion detection (default: 32)
noise_level 32
# Automatically tune the noise threshold (default: on)
noise_tune on
# Despeckle motion image using (e)rode or (d)ilate or (l)abel (Default: not defined)
# Recommended value is EedDl. Any combination (and number of) of E, e, d, and D is valid.
# (l)abeling must only be used once and the 'l' must be the last letter.
# Comment out to disable
despeckle_filter EedDl
# Detect motion in predefined areas (1 - 9). Areas are numbered like that: 1 2 3
# A script (on_area_detected) is started immediately when motion is 4 5 6
# detected in one of the given areas, but only once during an event. 7 8 9
# One or more areas can be specified with this option. Take care: This option
# does NOT restrict detection to these areas! (Default: not defined)
; area_detect value
# PGM file to use as a sensitivity mask.
# Full path name to. (Default: not defined)
; mask_file value
# PGM file to completely mask out a area of image.
# Full path name to. (Default: not defined)
# mask_privacy value
# Dynamically create a mask file during operation (default: 0)
# Adjust speed of mask changes from 0 (off) to 10 (fast)
smart_mask_speed 0
# Ignore sudden massive light intensity changes given as a percentage of the picture
# area that changed intensity. Valid range: 0 - 100 , default: 0 = disabled
lightswitch 0
# Picture frames must contain motion at least the specified number of frames
# in a row before they are detected as true motion. At the default of 1, all
# motion is detected. Valid range: 1 to thousands, recommended 1-5
minimum_motion_frames 1
# Specifies the number of pre-captured (buffered) pictures from before motion
# was detected that will be output at motion detection.
# Recommended range: 0 to 5 (default: 0)
# Do not use large values! Large values will cause Motion to skip video frames and
# cause unsmooth movies. To smooth movies use larger values of post_capture instead.
pre_capture 0
# Number of frames to capture after motion is no longer detected (default: 0)
post_capture 0
# Event Gap is the seconds of no motion detection that triggers the end of an event.
# An event is defined as a series of motion images taken within a short timeframe.
# Recommended value is 60 seconds (Default). The value -1 is allowed and disables
# events causing all Motion to be written to one single movie file and no pre_capture.
# If set to 0, motion is running in gapless mode. Movies don't have gaps anymore. An
# event ends right after no more motion is detected and post_capture is over.
event_gap 60
# Maximum length in seconds of a movie
# When value is exceeded a new movie file is created. (Default: 0 = infinite)
max_movie_time 0
# Always save images even if there was no motion (default: off)
emulate_motion off
############################################################
# Image File Output
############################################################
# Output 'normal' pictures when motion is detected (default: off)
# Valid values: on, off, first, best, center
# When set to 'first', only the first picture of an event is saved.
# Picture with most motion of an event is saved when set to 'best'.
# Picture with motion nearest center of picture is saved when set to 'center'.
# Can be used as preview shot for the corresponding movie.
output_pictures off
# Output pictures with only the pixels moving object (ghost images) (default: off)
output_debug_pictures off
# The quality (in percent) to be used by the jpeg and webp compression (default: 75)
quality 75
# Type of output images
# Valid values: jpeg, ppm or webp (default: jpeg)
picture_type jpeg
############################################################
# Use ffmpeg to encode videos of motion (default: off)
ffmpeg_output_movies on
# Use ffmpeg to make videos showing the moving pixels (ghost images) (default: off)
ffmpeg_output_debug_movies off
# Bitrate to be used by the ffmpeg encoder (default: 400000)
# This option is ignored if ffmpeg_variable_bitrate is not 0 (disabled)
ffmpeg_bps 400000
# Enables and defines variable bitrate for the ffmpeg encoder.
# ffmpeg_bps is ignored if variable bitrate is enabled.
# Valid values: 0 (default) = fixed bitrate defined by ffmpeg_bps,
# or the range 1 - 100 where 1 means worst quality and 100 is best.
ffmpeg_variable_bitrate 0
# Container/Codec output videos
# Valid values: mpeg4, msmpeg4, swf,flv, ffv1, mov, mp4, mkv, hevc
ffmpeg_video_codec mkv
# When creating videos, should frames be duplicated in order
# to keep up with the requested frames per second
# (default: true)
ffmpeg_duplicate_frames true
# Interval in seconds between timelapse captures. Default: 0 = off
timelapse_interval 0
# Timelapse file rollover mode. See motion_guide.html for options and uses.
timelapse_mode daily
# Frame rate for timelapse playback
timelapse_fps 30
# Container/Codec for timelapse video. Valid values: mpg or mpeg4
timelapse_codec mpg
############################################################
# External pipe to video encoder
# Replacement for FFMPEG builtin encoder for ffmpeg_output_movies only.
# The options movie_filename and timelapse_filename are also used
# by the ffmpeg feature
#############################################################
# Bool to enable or disable extpipe (default: off)
use_extpipe off
# External program (full path and opts) to pipe raw video to
# Generally, use '-' for STDIN...
;extpipe mencoder -demuxer rawvideo -rawvideo w=%w:h=%h:i420 -ovc x264 -x264encopts bframes=4:frameref=1:subq=1:scenecut=-1:nob_adapt:threads=1:keyint=1000:8x8dct:vbv_bufsize=4000:crf=24:partitions=i8x8,i4x4:vbv_maxrate=800:no-chroma-me -vf denoise3d=16:12:48:4,pp=lb -of avi -o %f.avi - -fps %fps
;extpipe x264 - --input-res %wx%h --fps %fps --bitrate 2000 --preset ultrafast --quiet -o %f.mp4
;extpipe mencoder -demuxer rawvideo -rawvideo w=%w:h=%h:fps=%fps -ovc x264 -x264encopts preset=ultrafast -of lavf -o %f.mp4 - -fps %fps
;extpipe ffmpeg -y -f rawvideo -pix_fmt yuv420p -video_size %wx%h -framerate %fps -i pipe:0 -vcodec libx264 -preset ultrafast -f mp4 %f.mp4
############################################################
# Snapshots (Traditional Periodic Webcam File Output)
############################################################
# Make automated snapshot every N seconds (default: 0 = disabled)
snapshot_interval 0
############################################################
# Text Display
# %Y = year, %m = month, %d = date,
# %H = hour, %M = minute, %S = second, %T = HH:MM:SS,
# %v = event, %q = frame number, %t = camera id number,
# %D = changed pixels, %N = noise level, \n = new line,
# %i and %J = width and height of motion area,
# %K and %L = X and Y coordinates of motion center
# %C = value defined by text_event - do not use with text_event!
# You can put quotation marks around the text to allow
# leading spaces
############################################################
# Locate and draw a box around the moving object.
# Valid values: on, off, preview (default: off)
# Set to 'preview' will only draw a box in preview_shot pictures.
locate_motion_mode off
# Set the look and style of the locate box if enabled.
# Valid values: box, redbox, cross, redcross (default: box)
# Set to 'box' will draw the traditional box.
# Set to 'redbox' will draw a red box.
# Set to 'cross' will draw a little cross to mark center.
# Set to 'redcross' will draw a little red cross to mark center.
locate_motion_style box
# Draws the timestamp using same options as C function strftime(3)
# Default: %Y-%m-%d\n%T = date in ISO format and time in 24 hour clock
# Text is placed in lower right corner
text_right %Y-%m-%d\n%T-%q
# Draw a user defined text on the images using same options as C function strftime(3)
# Default: Not defined = no text
# Text is placed in lower left corner
; text_left CAMERA %t
# Draw the number of changed pixed on the images (default: off)
# Will normally be set to off except when you setup and adjust the motion settings
# Text is placed in upper right corner
text_changes off
# This option defines the value of the special event conversion specifier %C
# You can use any conversion specifier in this option except %C. Date and time
# values are from the timestamp of the first image in the current event.
# Default: %Y%m%d%H%M%S
# The idea is that %C can be used filenames and text_left/right for creating
# a unique identifier for each event.
text_event %Y%m%d%H%M%S
# Draw characters at twice normal size on images. (default: off)
text_double off
# Text to include in a JPEG EXIF comment
# May be any text, including conversion specifiers.
# The EXIF timestamp is included independent of this text.
;exif_text %i%J/%K%L
############################################################
# Target Directories and filenames For Images And Films
# For the options snapshot_, picture_, movie_ and timelapse_filename
# you can use conversion specifiers
# %Y = year, %m = month, %d = date,
# %H = hour, %M = minute, %S = second,
# %v = event, %q = frame number, %t = camera id number,
# %D = changed pixels, %N = noise level,
# %i and %J = width and height of motion area,
# %K and %L = X and Y coordinates of motion center
# %C = value defined by text_event
# Quotation marks round string are allowed.
############################################################
# Target base directory for pictures and films
# Recommended to use absolute path. (Default: current working directory)
target_dir /var/lib/motion
# File path for snapshots (jpeg, ppm or webp) relative to target_dir
# Default: %v-%Y%m%d%H%M%S-snapshot
# Default value is equivalent to legacy oldlayout option
# For Motion 3.0 compatible mode choose: %Y/%m/%d/%H/%M/%S-snapshot
# File extension .jpg, .ppm or .webp is automatically added so do not include this.
# Note: A symbolic link called lastsnap.jpg created in the target_dir will always
# point to the latest snapshot, unless snapshot_filename is exactly 'lastsnap'
snapshot_filename %v-%Y%m%d%H%M%S-snapshot
# File path for motion triggered images (jpeg, ppm or .webp) relative to target_dir
# Default: %v-%Y%m%d%H%M%S-%q
# Default value is equivalent to legacy oldlayout option
# For Motion 3.0 compatible mode choose: %Y/%m/%d/%H/%M/%S-%q
# File extension .jpg, .ppm or .webp is automatically added so do not include this
# Set to 'preview' together with best-preview feature enables special naming
# convention for preview shots. See motion guide for details
picture_filename %v-%Y%m%d%H%M%S-%q
# File path for motion triggered ffmpeg films (movies) relative to target_dir
# Default: %v-%Y%m%d%H%M%S
# File extensions(.mpg .avi) are automatically added so do not include them
movie_filename %v-%Y%m%d%H%M%S
# File path for timelapse movies relative to target_dir
# Default: %Y%m%d-timelapse
# File extensions(.mpg .avi) are automatically added so do not include them
timelapse_filename %Y%m%d-timelapse
############################################################
# Global Network Options
############################################################
# Enable IPv6 (default: off)
ipv6_enabled off
############################################################
# Live Stream Server
############################################################
# The mini-http server listens to this port for requests (default: 0 = disabled)
stream_port 8081
# 50% scaled down substream (default: 0 = disabled)
# substream_port 8082
# Quality of the jpeg (in percent) images produced (default: 50)
stream_quality 50
# Output frames at 1 fps when no motion is detected and increase to the
# rate given by stream_maxrate when motion is detected (default: off)
stream_motion off
# Maximum framerate for stream streams (default: 1)
stream_maxrate 1
# Restrict stream connections to localhost only (default: on)
stream_localhost on
# Limits the number of images per connection (default: 0 = unlimited)
# Number can be defined by multiplying actual stream rate by desired number of seconds
# Actual stream rate is the smallest of the numbers framerate and stream_maxrate
stream_limit 0
# Set the authentication method (default: 0)
# 0 = disabled
# 1 = Basic authentication
# 2 = MD5 digest (the safer authentication)
stream_auth_method 0
# Authentication for the stream. Syntax username:password
# Default: not defined (Disabled)
; stream_authentication username:password
# Percentage to scale the stream image for preview
# This is scaled on the browser side, motion will keep sending full frames
# Default: 25
; stream_preview_scale 25
# Have stream preview image start on a new line
# Default: no
; stream_preview_newline no
############################################################
# HTTP Based Control
############################################################
# TCP/IP port for the http server to listen on (default: 0 = disabled)
webcontrol_port 8080
# Restrict control connections to localhost only (default: on)
webcontrol_localhost on
# Output for http server, select off to choose raw text plain (default: on)
webcontrol_html_output on
# Authentication for the http based control. Syntax username:password
# Default: not defined (Disabled)
; webcontrol_authentication username:password
# Parameters to include on webcontrol. 0=none, 1=limited, 2=advanced, 3=restricted
# Default: 0 (none)
webcontrol_parms 0
############################################################
# Tracking (Pan/Tilt)
#############################################################
# Type of tracker (0=none (default), 1=stepper, 2=iomojo, 3=pwc, 4=generic, 5=uvcvideo, 6=servo)
# The generic type enables the definition of motion center and motion size to
# be used with the conversion specifiers for options like on_motion_detected
track_type 0
# Enable auto tracking (default: off)
track_auto off
# Serial port of motor (default: none)
;track_port /dev/ttyS0
# Motor number for x-axis (default: 0)
;track_motorx 0
# Set motorx reverse (default: 0)
;track_motorx_reverse 0
# Motor number for y-axis (default: 0)
;track_motory 1
# Set motory reverse (default: 0)
;track_motory_reverse 0
# Maximum value on x-axis (default: 0)
;track_maxx 200
# Minimum value on x-axis (default: 0)
;track_minx 50
# Maximum value on y-axis (default: 0)
;track_maxy 200
# Minimum value on y-axis (default: 0)
;track_miny 50
# Center value on x-axis (default: 0)
;track_homex 128
# Center value on y-axis (default: 0)
;track_homey 128
# ID of an iomojo camera if used (default: 0)
track_iomojo_id 0
# Angle in degrees the camera moves per step on the X-axis
# with auto-track (default: 10)
# Currently only used with pwc type cameras
track_step_angle_x 10
# Angle in degrees the camera moves per step on the Y-axis
# with auto-track (default: 10)
# Currently only used with pwc type cameras
track_step_angle_y 10
# Delay to wait for after tracking movement as number
# of picture frames (default: 10)
track_move_wait 10
# Speed to set the motor to (stepper motor option) (default: 255)
track_speed 255
# Number of steps to make (stepper motor option) (default: 40)
track_stepsize 40
############################################################
# External Commands, Warnings and Logging:
# You can use conversion specifiers for the on_xxxx commands
# %Y = year, %m = month, %d = date,
# %H = hour, %M = minute, %S = second,
# %v = event, %q = frame number, %t = camera id number,
# %D = changed pixels, %N = noise level,
# %i and %J = width and height of motion area,
# %K and %L = X and Y coordinates of motion center
# %C = value defined by text_event
# %f = filename with full path
# %n = number indicating filetype
# Both %f and %n are only defined for on_picture_save,
# on_movie_start and on_movie_end
# Quotation marks round string are allowed.
############################################################
# Do not sound beeps when detecting motion (default: on)
# Note: Motion never beeps when running in daemon mode.
quiet on
# Command to be executed when an event starts. (default: none)
# An event starts at first motion detected after a period of no motion defined by event_gap
; on_event_start value
# Command to be executed when an event ends after a period of no motion
# (default: none). The period of no motion is defined by option event_gap.
; on_event_end value
# Command to be executed when a picture (.ppm|.jpg) is saved (default: none)
# To give the filename as an argument to a command append it with %f
; on_picture_save value
# Command to be executed when a motion frame is detected (default: none)
; on_motion_detected value
# Command to be executed when motion in a predefined area is detected
# Check option 'area_detect'. (default: none)
; on_area_detected value
# Command to be executed when a movie file (.mpg|.avi) is created. (default: none)
# To give the filename as an argument to a command append it with %f
; on_movie_start value
# Command to be executed when a movie file (.mpg|.avi) is closed. (default: none)
# To give the filename as an argument to a command append it with %f
; on_movie_end value
# Command to be executed when a camera can't be opened or if it is lost
# NOTE: There is situations when motion don't detect a lost camera!
# It depends on the driver, some drivers dosn't detect a lost camera at all
# Some hangs the motion thread. Some even hangs the PC! (default: none)
; on_camera_lost value
# Command to be executed when a camera that was lost has been found (default: none)
# NOTE: If motion doesn't properly detect a lost camera, it also won't know it found one.
; on_camera_found value
#####################################################################
# Common Options for database features.
# Options require database options to be active also.
#####################################################################
# Log to the database when creating motion triggered picture file (default: on)
; sql_log_picture on
# Log to the database when creating a snapshot image file (default: on)
; sql_log_snapshot on
# Log to the database when creating motion triggered movie file (default: off)
; sql_log_movie off
# Log to the database when creating timelapse movies file (default: off)
; sql_log_timelapse off
# SQL query string that is sent to the database
# Use same conversion specifiers has for text features
# Additional special conversion specifiers are
# %n = the number representing the file_type
# %f = filename with full path
# Default value:
# Create tables :
##
# Mysql
# CREATE TABLE security (camera int, filename char(80) not null, frame int, file_type int, time_stamp timestamp(14), event_time_stamp timestamp(14));
#
# Postgresql
# CREATE TABLE security (camera int, filename char(80) not null, frame int, file_type int, time_stamp timestamp without time zone, event_time_stamp timestamp without time zone);
#
# insert into security(camera, filename, frame, file_type, time_stamp, text_event) values('%t', '%f', '%q', '%n', '%Y-%m-%d %T', '%C')
; sql_query insert into security(camera, filename, frame, file_type, time_stamp, event_time_stamp) values('%t', '%f', '%q', '%n', '%Y-%m-%d %T', '%C')
############################################################
# Database Options
############################################################
# database type : mysql, postgresql, sqlite3 (default : not defined)
; database_type value
# database to log to (default: not defined)
# for sqlite3, the full path and name for the database.
; database_dbname value
# The host on which the database is located (default: localhost)
; database_host value
# User account name for database (default: not defined)
; database_user value
# User password for database (default: not defined)
; database_password value
# Port on which the database is located
# mysql 3306 , postgresql 5432 (default: not defined)
; database_port value
# Database wait time in milliseconds for locked database to
# be unlocked before returning database locked error (default 0)
; database_busy_timeout 0
############################################################
# Video Loopback Device (vloopback project)
############################################################
# Output images to a video4linux loopback device
# Specify the device associated with the loopback device
# For example /dev/video1 (default: not defined)
; video_pipe value
# Output motion images to a video4linux loopback device
# Specify the device associated with the loopback device
# For example /dev/video1 (default: not defined)
; motion_video_pipe value
##############################################################
# camera config files - One for each camera.
# Except if only one camera - You only need this config file.
# If you have more than one camera you MUST define one camera
# config file for each camera in addition to this config file.
##############################################################
# Remember: If you have more than one camera you must have one
# camera file for each camera. E.g. 2 cameras requires 3 files:
# This motion.conf file AND camera1.conf and camera2.conf.
# Only put the options that are unique to each camera in the
# camera config files.
; camera /etc/motion/camera1.conf
; camera /etc/motion/camera2.conf
; camera /etc/motion/camera3.conf
; camera /etc/motion/camera4.conf
##############################################################
# Camera config directory
# Any files ending in '.conf' in this directory will be read
# as a camera config file.
##############################################################
; camera_dir /etc/motion/conf.d